Recognizing the signs of oral cancer is crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into understanding oral cancer, its common symptoms, and underlying risk factors. Learn to identify unusual changes in your mouth and throat, and discover how regular dental check-ups play a vital role in early identification. Additionally, explore treatment options and support available for those facing this challenging condition, emphasizing the importance of proactive health management.
Understanding Oral Cancer: A Comprehensive Overview
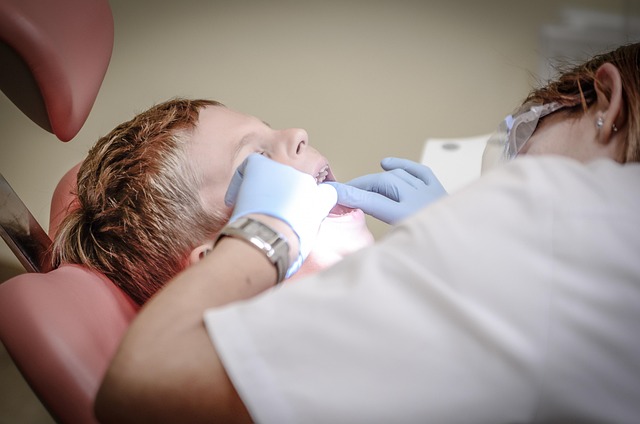
Oral cancer, a term that encompasses cancers forming in the mouth, lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat, is a significant health concern. It’s crucial to understand that early detection plays a pivotal role in successful treatment outcomes. Awareness of both subtle and apparent symptoms can facilitate prompt medical intervention.
This comprehensive overview highlights the importance of recognizing various signs, including unusual lesions or sores, red or white patches in the mouth, altered sensations like numbness or tingling, and persistent pain or swelling. By familiarizing yourself with these indicators, you empower yourself and others to take proactive measures against oral cancer.
Common Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Oral cancer, like any other form, can be challenging to detect early on, but being aware of the common signs and symptoms is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Some telltale indicators include persistent mouth sores or ulcers that do not heal within two weeks, red or white patches in the mouth or on the tongue, unusual bleeding in the oral cavity, and swollen lymph nodes.
Changes in the lips, such as redness, soreness, or thickening, can also be early warning signs. If you notice any of these symptoms lasting for more than two weeks, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional. They may refer you to an oral surgeon or oncologist who specializes in oral cancer for further evaluation and proper care.
Risk Factors and Potential Causes Explored
Oral cancer, a serious condition affecting millions globally, arises from a complex interplay of risk factors and potential causes. Smokers and heavy drinkers are at elevated risk due to the damaging effects of tobacco and alcohol on oral cells. Chronic exposure to UV radiation from sunlight can also lead to oral cancer, particularly in regions with high ultraviolet index. Additionally, certain viral infections like human papillomavirus (HPV) have been linked to a higher incidence rate. Genetic predispositions play a role too; individuals with a family history of oral cancer may be more susceptible. Furthermore, long-term use of betel quid or areca nut, common in some cultures, significantly increases the likelihood of developing this disease. Understanding these risk factors is crucial for early detection and effective prevention strategies.
Early Detection: The Power of Regular Dental Check-ups
Early detection is a cornerstone in the battle against oral cancer, and regular dental check-ups play a pivotal role. During these appointments, dentists are trained to spot subtle changes in your oral cavity that might indicate potential cancerous growths. They examine your gums, tongue, cheeks, lips, and throat for any abnormal lesions, red or white patches, or moles that look different from usual. These regular visits can provide life-saving benefits as early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
By staying on top of dental check-ups, you empower your dentist to detect oral cancer at its most treatable stages. This proactive approach allows for less invasive procedures and often leads to better overall health outcomes. So, don’t underestimate the power of a simple dental visit; it could be the key to identifying and addressing potential oral cancer symptoms before they become more serious.
Treatment Options and Support for Oral Cancer Patients

Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health. Early-stage tumors may be treated with surgery to remove the lesion, followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy to eliminate any remaining cells. For more advanced cancers, a combination of treatments like surgical resection, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy might be employed. These approaches aim to destroy cancerous cells while minimizing damage to healthy tissues.
Support for oral cancer patients is crucial throughout their journey. This includes emotional support from family and friends, as well as access to specialized care teams comprising oncologists, oral surgeons, radiation therapists, and counselors. Support groups and patient advocacy organizations also play a vital role by providing a network of peers who have experienced similar challenges. These resources help patients cope with the physical and psychological effects of cancer treatment, enhancing their quality of life.
Oral cancer is a serious yet often overlooked health issue, emphasizing the crucial role regular dental check-ups play in early detection. By familiarizing ourselves with common signs and symptoms, such as persistent mouth sores or changes in oral tissues, we can significantly improve outcomes. Understanding risk factors and potential causes enables us to make informed decisions about our oral health. With advanced treatment options available, support for patients is more comprehensive than ever before, offering hope and improved quality of life. Let’s prioritize our oral health and be vigilant against oral cancer.
