Oral cancer, a silent yet aggressive health threat, demands our attention. Understanding its causes and risk factors is the first step towards early detection. This article guides you through the intricate world of oral cancer, focusing on recognizing subtle symptoms often overlooked. From understanding the disease to exploring diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management, we empower you with knowledge. Learn how to identify common oral cancer signs and take proactive steps towards a healthier mouth.
Understanding Oral Cancer: Causes and Risk Factors

Oral cancer, a serious condition that affects millions worldwide, arises from the abnormal growth of cells within the mouth and throat. Unlike other forms of cancer, it’s often visible to the naked eye, presenting distinct symptoms that, if recognized early, can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with oral cancer is crucial for prompt detection and effective management.
The primary risk factors include persistent oral infections, such as periodontal disease and mouth sores; tobacco use, including smoking and chewing tobacco; excessive alcohol consumption; sun exposure, particularly to the lips; a history of head or neck radiation therapy; and a weakened immune system. Genetic predispositions also play a role, with certain hereditary conditions increasing susceptibility. By recognizing these factors and being vigilant for symptoms like persistent mouth sores, red or white patches in the mouth, lump formation, and unusual bleeding or swelling, individuals can take proactive measures to detect oral cancer at an early stage.
Recognizing Early Signs and Symptoms

Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, is more treatable when detected early. Recognizing subtle changes in your mouth and throat can be crucial. Common early signs include persistent mouth sores, red or white patches on the lips, gums, or tongue, and unusual bleeding that doesn’t heal. These symptoms might not always indicate oral cancer, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Additionally, look out for swollen lymph nodes in the neck, difficulty swallowing, changes in voice, and unexplained weight loss. Regular dental check-ups are vital in monitoring these signs. Early detection allows for more effective treatment options and improves the chances of a successful outcome.
Common Oral Cancer Symptoms to Watch For

Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, has distinct symptoms that can be recognized early on. Some common signs to watch for include persistent mouth sores or lesions that do not heal after a couple of weeks, red or white patches in the mouth, unusual bleeding, swelling or lumps in the jawline, gums or inside the cheeks, and pain or difficulty swallowing or moving the jaw.
Changes in your teeth are also indicative of potential oral cancer. This could be loose teeth, sudden tooth sensitivity, or an altered bite. Additionally, chronic bad breath that doesn’t go away with mouthwash or improved hygiene can be an early warning sign. If you notice any of these symptoms persisting for more than two weeks, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional as they may refer you to a specialist for further evaluation and testing.
Diagnosis and Staging of Oral Cancers
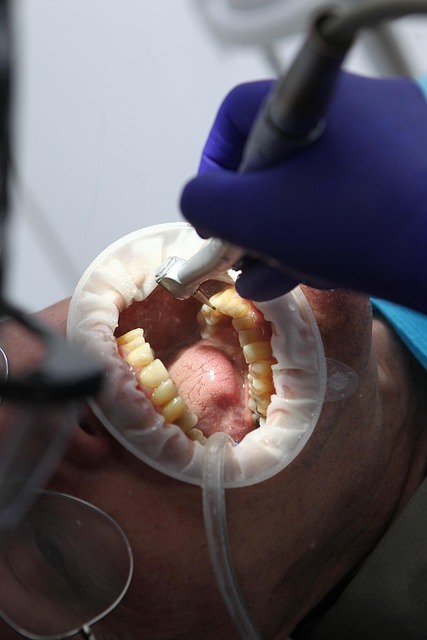
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, requires early detection for successful treatment. Diagnosis begins with a thorough examination of the mouth by a dental professional or medical oncologist. They look for visual signs such as lesions, ulcers, or discolored patches that do not heal within two weeks. Biopsies are performed to take tissue samples from suspicious areas and test for cancerous cells. Once diagnosed, oral cancers are staged based on their size, location, and extent of spread. Staging helps determine the severity of the disease and guides treatment decisions, which can include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Early-stage oral cancers often respond well to treatment, emphasizing the importance of regular dental check-ups and recognizing symptoms promptly.
Treatment Options and Long-Term Management
Treatment options for oral cancer vary based on the stage and location of the tumor. Early-stage cancers are often treated with surgery to remove the affected tissue, followed by radiation therapy or chemotherapy to destroy any remaining cancer cells. Advanced-stage tumors might require a combination of treatments, including targeted therapies and immunotherapies. These modern approaches aim to minimize side effects while maximizing effectiveness.
Long-term management involves regular check-ups and follow-up care to monitor for recurrence. This includes dental exams, screenings, and imaging tests. Supportive care, such as speech therapy or nutrition counseling, can also be crucial for patients’ overall well-being. By staying vigilant and adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with oral cancer can achieve long-term remission and improve their quality of life.
Oral cancer, though often overlooked, is a serious condition with significant implications. By understanding its causes, recognizing early symptoms, and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can significantly improve their chances of successful treatment. Remember, timely diagnosis is key in managing oral cancer effectively. Regular check-ups and staying vigilant for any unusual changes in your mouth are essential steps towards maintaining good oral health.
