Toothache Symptoms: Unmasking Dental Issues
A toothache can be a persistent and debilitating pain, but understanding its underlying causes is key to effective treatment. This article guides you through deciphering toothache symptoms, from pinpointing acute or recurring pain to recognizing risk factors. We explore the varying types of dental discomfort, analyzing pain patterns and accompanying oral/systemic signs. Learn how to navigate diagnosis, discover therapeutic options, and embrace preventive care for long-term dental wellness. Uncover the clues your teeth offer by delving into this comprehensive guide on toothache symptoms.
Understanding Toothache: Common Causes and Risk Factors
Toothaches are a common dental concern, often indicating an underlying issue that requires attention. Understanding the symptoms and potential causes is the first step in effective management. The pain associated with toothaches can range from mild to severe, typically localized to a specific tooth or area of the mouth. Common triggers include dental caries (cavities), gum disease, tooth fragment fractures, or even simple inflammation of the pulp inside the tooth.
Risk factors contributing to toothache symptoms may include poor oral hygiene, dietary habits rich in sugars and acids, previous dental procedures, age-related changes in teeth and gums, and certain medical conditions affecting the mouth and teeth. Recognizing these factors can help individuals proactively address potential issues, ultimately preventing more severe dental problems and discomfort.
– Identifying recurring and acute toothache cases

Toothaches can be either recurrent or acute, each presenting distinct patterns and offering valuable clues about potential dental issues. Recurrent toothaches are characterized by persistent pain that comes and goes over time. This type of toothache often signals chronic problems like dental caries (cavities), periodontal disease (gum disease), or even an abfraction—a small crack in the tooth’s enamel due to clenching or grinding. Such recurring pain may be triggered by certain foods, temperatures, or even stress.
On the other hand, acute toothaches are intense and sudden, usually indicating a more urgent dental issue. This can be caused by severe decay, an abscessed tooth, or even a fractured tooth. The pain is often debilitating and may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck. Prompt action is required for acute toothaches as they require immediate dental attention to prevent further complications.
– Demystifying common risk factors for dental issues

Toothaches are often signs of underlying dental problems, and understanding risk factors can help in early detection. Common culprits include poor oral hygiene, where plaque buildup on teeth leads to gum inflammation and potential tooth decay. Age is also a factor; as we age, our gums may recede, exposing roots more susceptible to sensitivity and infection. Diet plays a significant role too; frequent consumption of sugary foods and drinks fuels bacteria growth, contributing to caries and tooth erosion. Additionally, certain medical conditions like dry mouth (xerostomia) reduce saliva production, creating an ideal environment for bacterial overgrowth and dental issues.
Other risk factors include genetic predisposition, as some individuals are more susceptible to gum disease or tooth decay due to their DNA. Lifestyle choices such as smoking can also exacerbate oral health problems. Understanding these risks is vital in managing toothache symptoms effectively and preventing further complications.
Pain Patterns: Decoding the Messages Your Teeth Send
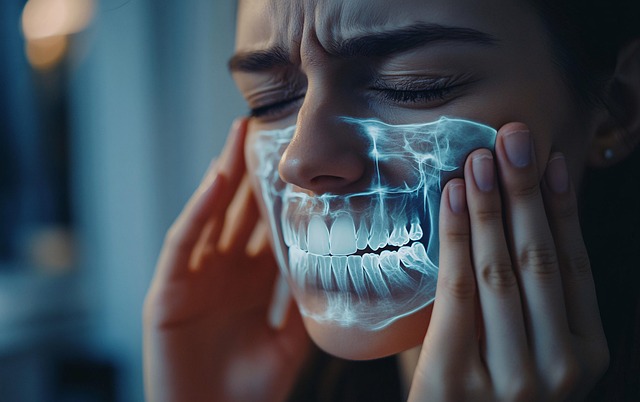

Toothache symptoms can offer valuable clues about what’s happening beneath the surface. The pattern of pain—when it occurs, how intense it is, and where exactly it feels—can provide essential information about the underlying dental issue. For example, a sharp, sudden ache that radiates to your jaw or ear could indicate an abscessed tooth, while persistent, dull pain focused in one specific tooth might suggest decay. By paying attention to these pain patterns, you can prioritize your dental health and address issues early, preventing more serious complications.
Understanding toothache symptoms is key to identifying potential dental problems early. By recognizing recurring or acute pain, along with associated risk factors, individuals can take proactive measures to maintain oral health. Decoding the unique ‘language’ of pain signals from your teeth allows for timely interventions, preventing minor issues from becoming major concerns. Knowing these toothache symptoms can empower folks to navigate their dental care needs effectively.
