Oral cancer, often overlooked, can be a devastating diagnosis if detected late. Learn how to identify early signs and symptoms for swift action. This comprehensive guide covers understanding oral cancer, recognizing subtle changes in your mouth, and identifying those at highest risk. Discover various diagnosis techniques, from simple visual exams to advanced scanning technologies. Explore treatment options and preventive strategies to minimize chances of developing this disease. Early detection saves lives—be proactive about your oral health.
Understanding Oral Cancer: What You Need to Know
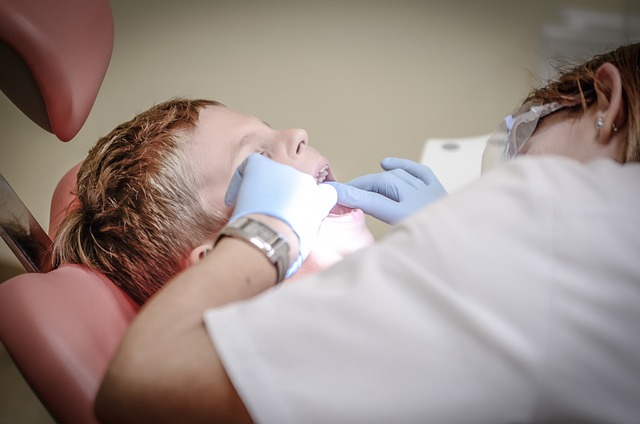
Oral cancer, a term that encompasses cancers forming in the mouth, throat, and nearby structures, is a serious yet often overlooked health concern. It’s crucial to understand that early detection plays a pivotal role in improving treatment outcomes. By familiarizing yourself with the signs and symptoms, you can be better equipped to identify potential issues at their nascent stages.
Knowing the risk factors associated with oral cancer is equally important. These include smoking or chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption, and exposure to certain viruses. Regular oral examinations by dental professionals are recommended, as they can spot abnormalities that might indicate early-stage oral cancer. Stay vigilant for any persistent sores, lumps, or discolored patches in the mouth, and don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare provider if you notice any concerning changes.
Recognizing Early Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing early signs and symptoms of oral cancer is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Keep an eye out for any unusual changes in your mouth, including persistent sores, red or white patches, or swollen lymph nodes. These could be indicators of a developing issue. Additionally, look for spots or lesions that do not heal within two weeks, as this may point to the presence of oral cancer.
Regular self-exams and dental visits are essential tools in early detection. During these check-ups, dentists can carefully examine your mouth for any unusual growths or abnormalities. Don’t hesitate to voice any concerns you might have regarding potential symptoms, as early intervention significantly improves outcomes for oral cancer patients.
Risk Factors and Who is Most Vulnerable
Oral cancer, like any other form of cancer, has specific risk factors that can indicate an increased vulnerability to developing the disease. Age is a significant factor; the risk of oral cancer tends to rise with age, with the majority of cases diagnosed in people over 40. Gender also plays a role, as men are slightly more prone to oral cancer than women.
Other essential considerations include tobacco use, both smoking and chewing, which significantly elevate the risk. Excessive alcohol consumption is another known contributor. Additionally, a history of previous oral cancer or chronic conditions like oral leukoplakia can increase susceptibility. Certain rare genetic syndromes and a weakened immune system due to HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive treatments are also linked to higher rates of oral cancer development.
Diagnosis: Testing and Scanning Techniques
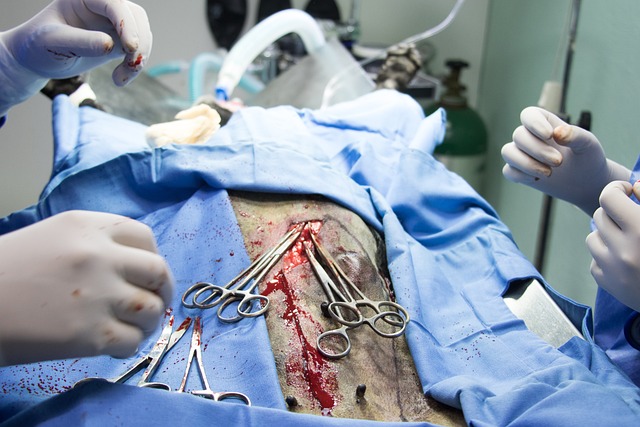
Early detection is crucial in fighting oral cancer, and an important step in this process involves various testing and scanning techniques. Dentists will often perform a thorough examination of your mouth, including checking for any abnormal lumps, spots, or lesions that could be indicative of oral cancer. They might use specialized tools to gently palpate the tissues and take a close look at hard-to-reach areas.
Advanced diagnostic tools include imaging scans such as X-rays, CT (computer tomography) scans, and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). These techniques help identify potential tumors or abnormalities that may not be visible during a manual exam. For example, an X-ray can reveal bone erosion, while an MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, aiding in the early detection of oral cancer and ensuring prompt treatment.
Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies

Early detection is key in improving outcomes for oral cancer patients, as it allows for more effective treatment strategies. If caught at an early stage, when the tumor is small and has not spread, surgery is often the primary treatment option. This may involve removing the cancerous tissue and surrounding areas to ensure complete removal of the tumor. In some cases, radiation therapy or chemotherapy might be recommended post-surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
Prevention strategies for oral cancer focus on reducing risk factors. Regular dental check-ups are crucial as dentists can identify early signs and symptoms that may indicate oral cancer. Staying away from tobacco products, limiting alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits and vegetables are all essential preventive measures. Additionally, understanding and avoiding sun exposure without protection can help reduce the risk, as UV radiation has been linked to certain types of oral cancer.
Early detection of oral cancer is key to improving outcomes and quality of life. By understanding the signs, recognizing your risk factors, and staying vigilant, you can play a crucial role in catching this disease at its most treatable stages. Don’t overlook any unusual changes in your mouth—they may be early indicators that require further evaluation. With proper care and regular check-ups, it’s possible to prevent or manage oral cancer effectively.
